In C++, two or more functions can used the same name as long
as their parameter declarations are different.
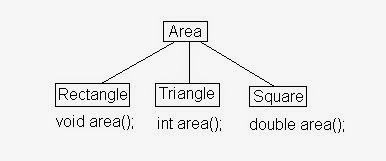
In this situation, the functions used the same name are said
to be overloaded, and the process is referred to as function overloading.
In the function overloading the functions used in program
has the same name with different return data type, different arguments, and
different order of arguments.
Example:
Advantages of Function
Overloading
1.
Eliminating the use of the different function
name for same operation.
2.
Help to understand, debug and group easily.
3.
Easy maintainability of the code.
Example
of Function Overloading
Write
C++ Program to calculate the area of rectangle and circle with the same
function name.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class shape
{
double
length, breadth, ar;
public:
void
area();
double
area(double r);
};
void shape :: area ()
{
cout<<”Enter
the length and breadth = ”;
cin>>
length>>breadth;
ar=
length*breadth;
cout<<” Area of Rectangle = ”;
cout<<
ar;
}
double shap :: area (double r)
{
return
3.14*r*r;
}
void main()
{
clrscr
();
shape s;
s.area();
double
K, t;
cout<<”Enter
the radius = ”;
cin>>t;
K=s.area(t);
cout<<” Area of Circle = ”;
cout<<K;
getch();
}
Example
of Function Overloading
Write
C++ Program to overload the volume for finding the volume of the following
shapes:
·
Cube:
(a*a*a),
·
Rectangle:
(l*b*h).
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
class shape
{
double
a, h, l, b, vol;
public:
void
volume ();
float
volume (float r, float h);
double
volume( double l, double b, double h);
};
void shape :: volume
{
cout<<”Enter
the length of any edge of the cube”;
cin>>a;
vol=a*a*a;
cout<<”Volume
of cube = ”;
cout<<vol;
}
float shape :: volume (float r, float r)
{
return 3.14*r*r*h;
}
double shape :: volume (double l, double b, double h)
{
return l*b*h;
}
void main()
{
clrscr ();
double K, t, r, h;
shape s;
s.volume ();
cout<<”Enter
radius and height of Cylinder = ”;
cin>>r>>h;
k = s.volume (r,
h);
cout<<”Volume
of Cylinder = ”;
cout<<”Enter
length, breadth and height of Rectangle = ”;
cin>>l>>b>>h;
t = s.volume (l,
b, h);
cout<<” Volume
of Rectangle”;
cout<<t;
getch();
}
 ),
),
No comments:
Post a Comment